Commercial Real Estate Due Diligence Checklist: 7 Key Steps
Commercial Real Estate Due Diligence Checklist: 7 Key Steps
Ensure smart investments with our commercial real estate due diligence checklist. Discover insider tips to mitigate risks and maximize returns.
Domingo Valadez
May 6, 2025
Blog
Investing Wisely in Commercial Real Estate: Start Here
Commercial real estate presents lucrative opportunities for substantial returns. However, it's a complex market with potential risks. Navigating this environment successfully requires a thorough and systematic approach to due diligence. This process has changed considerably over time, influenced by market fluctuations and lessons learned. From the simplest property transactions to today’s complex investment strategies, one thing remains the same: well-informed decisions reduce risk and maximize profit.
What used to be a relatively straightforward process of confirming ownership and evaluating the physical condition of a property has become a multifaceted investigation. Modern due diligence includes financial, legal, environmental, and market analysis.
The effectiveness of any due diligence approach depends on its thoroughness. A fragmented approach that overlooks critical aspects can expose investors to unforeseen problems. These problems can put the entire investment at risk. Think of it like building construction: a strong foundation is crucial. Ignoring key structural elements in the beginning can result in major issues later on. Similarly, neglecting essential components of due diligence can undermine even the most promising commercial real estate ventures.
This 7-point checklist, based on industry best practices and decades of experience, provides a solid framework for evaluating potential investments.
Understanding the 7-Point Checklist
In this article, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive 7-point checklist that addresses all the vital aspects of commercial real estate due diligence. This ranges from the detailed analysis of financial performance to the broader perspective of market tendencies. By understanding and implementing these principles, you’ll be well-equipped to make informed investment decisions. You'll also minimize potential risks and position yourself for long-term success in the competitive commercial real estate market.
1. Financial Analysis and Review

Financial analysis and review is the most critical aspect of commercial real estate due diligence. It provides the concrete, data-driven foundation for informed investment decisions. This process involves examining the target property's financial performance, giving investors a clear understanding of its current financial health and future earning potential. It's the first step in due diligence because it directly impacts an investor's potential return and mitigates financial risks.
For real estate syndicators, multifamily investors, and sponsors, understanding a property's financial intricacies is paramount. This analysis goes beyond the asking price; it digs deep into the numbers to uncover the true value and potential risks.
Key Features of a Thorough Financial Analysis
A robust financial analysis should include several key components:
- Income and Expense Statements (2-3 Years): Analyzing historical trends in income and expenses helps identify strengths and weaknesses in the property's operations.
- Rent Roll Analysis with Tenant Payment History: This provides insights into tenant quality, lease terms, and future income streams. Understanding tenant reliability is crucial for accurate cash flow projections.
- Operating Expense Analysis and Comparison to Industry Benchmarks: Comparing operating expenses against benchmarks (e.g., provided by the Building Owners and Managers Association (BOMA)) lets investors assess the efficiency of property management and identify potential cost optimization areas.
- Cap Rate Calculation and Cash Flow Projections: These metrics are essential for evaluating the property's potential return on investment and determining its overall financial viability.
- Tax Assessment Records and History of Property Tax Increases: Understanding the property tax burden, both current and historical, is vital for accurate financial forecasting.
Pros of Financial Analysis
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Financial analysis provides concrete data for informed decisions, reducing reliance on speculation.
- Early Identification of Red Flags: Thorough analysis can uncover potential issues, like high operating expenses or declining rental income, allowing investors to make informed decisions.
- Accurate ROI Forecasting: By analyzing historical data and projecting future performance, investors can develop realistic ROI expectations.
- Streamlined Financing: A well-prepared financial analysis is crucial for securing financing from lenders.
Cons of Financial Analysis
- Past Performance Doesn't Guarantee Future Results: While historical data is valuable, market conditions and unexpected expenses can impact future performance.
- Potential for Data Manipulation: Sellers might present data selectively. Independent verification is crucial.
- Requires Specialized Knowledge: Interpreting financial statements and performing calculations requires expertise. Engaging experienced professionals can ensure accuracy.
Real-World Examples
- Blackstone's Acquisition of Stuyvesant Town-Peter Cooper Village: This case highlights the importance of due diligence. Blackstone's analysis revealed untapped income potential through renovations.
- WeWork's Failed IPO: This serves as a cautionary tale of inadequate due diligence. Rigorous analysis could have potentially revealed the company's unsustainable financial model.
Practical Tips for Implementation
- Verify Information with Third-Party Sources: Independently verify data with sources like property tax assessors and utility companies.
- Use Industry Benchmarks: Compare the property's operating expenses to industry benchmarks (e.g., BOMA standards) to assess its efficiency.
- Request Utility Bills Directly: Obtain utility bills directly from providers for accuracy and transparency.
- Scenario Planning: Calculate multiple financial scenarios (best case, worst case, most likely) to understand the potential range of outcomes.
Organizations and Best Practices
Organizations like the CCIM Institute, the Urban Land Institute (ULI), and PwC Real Estate Investor Survey methodology have popularized financial due diligence best practices.
By prioritizing financial analysis, real estate investors can make data-driven decisions, mitigate risks, and maximize the potential for profitable investments.
2. Physical Property Inspection
A crucial step in commercial real estate due diligence is the Physical Property Inspection. This involves a thorough examination of the property's physical state, covering everything from the foundation and roof to the HVAC system and plumbing. For real estate syndicators, multifamily investors, and sponsors, this step is essential for mitigating risk and maximizing returns.

Understanding the property's physical condition allows for well-informed decision-making, accurate budgeting, and potentially substantial cost savings in the future. This inspection helps uncover necessary repairs, ongoing maintenance needs, and potential capital expenditures that could significantly impact the property’s value and future operating expenses.
What a Physical Property Inspection Includes
A detailed assessment typically covers the following areas:
- Structural Assessment: Evaluating the foundation, walls, roof, and other structural elements for stability and soundness.
- Building Systems Evaluation: Analyzing the performance and state of crucial systems such as HVAC, electrical, plumbing, and fire safety.
- Environmental Hazard Identification: Screening for environmental concerns like asbestos, lead paint, or mold.
- ADA Compliance Assessment: Verifying compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act accessibility guidelines.
- Building Code Compliance Review: Ensuring the property adheres to current building codes and regulations.
Why a Physical Property Inspection Matters
A comprehensive physical inspection provides a clear understanding of the property's actual condition, enabling investors to make informed choices. This translates to several key benefits:
Pros:
- Early Identification of Costly Repairs: Discovering hidden problems allows you to negotiate a better price or avoid a potentially poor investment.
- Negotiation Leverage: Documented issues give you concrete justification to request price adjustments.
- Accurate Capital Expenditure Budgets: Anticipating necessary repairs and improvements facilitates accurate budgeting and financial planning.
- Reduced Risk of Unexpected Expenses: Minimizes the chance of unforeseen and potentially budget-breaking repairs after acquisition.
Cons:
- Expense: Comprehensive inspections, particularly for large properties or those needing specialized expertise, can be costly.
- Potential for Undetected Issues: Some hidden problems might remain undetected even with a thorough inspection.
- Time Commitment: Inspections can be time-consuming and may potentially delay the closing process.
- Need for Multiple Specialists: Different aspects of the inspection may require specialized professionals (e.g., structural engineer, environmental consultant).
Real-World Examples and Industry Standards
Real-world examples demonstrate the value of thorough inspections. For instance, due diligence by Jones Lang LaSalle uncovered significant structural issues leading to a substantial price reduction. Boston Properties utilizes infrared scanning to proactively identify potential problems.
Organizations like the American Society of Home Inspectors (ASHI), BOMA International, and ASTM International have established standards and best practices for property condition assessments, increasing the professionalism and dependability of commercial property inspections.
Tips for Effective Implementation
- Experienced Inspectors: Engage inspectors with proven commercial real estate experience.
- Capital Expenditure History: Request a capital expenditure history spanning the past 5-10 years for insight into recurring problems.
- Varied Weather Conditions: Conduct inspections during different weather conditions if possible to reveal issues that might be missed otherwise.
- Video Documentation: Create a video record of the inspection for future reference and documentation.
- Review Records: Examine maintenance logs and service contracts for valuable information.
By prioritizing the Physical Property Inspection, real estate professionals can minimize risks, negotiate effectively, and make informed investment decisions that contribute to lasting success.
3. Environmental Due Diligence
Environmental due diligence is a critical component of any commercial real estate transaction. It's a thorough investigation of a property to identify potential environmental hazards, contamination, or compliance issues. These issues could impact the property's value, usability, or create future liabilities. This process protects investors from unexpected costs and legal problems associated with environmental issues. For real estate syndicators, multifamily investors, and sponsors, neglecting this due diligence can have serious financial and legal consequences.

The core of environmental due diligence typically involves Phase I and potentially Phase II Environmental Site Assessments (ESAs). A Phase I ESA primarily involves a historical review of the property, a site inspection, and interviews with current and former occupants and neighbors. This aims to identify Recognized Environmental Conditions (RECs). RECs are past or current uses that suggest the presence, or potential presence, of hazardous substances or petroleum products.
If RECs are discovered during Phase I, a Phase II ESA might be necessary. This phase involves taking samples and conducting laboratory analysis. Soil, groundwater, and sometimes air, are tested to confirm the presence and extent of contamination. Depending on the property's location and history, other evaluations might be needed. These can include assessments for asbestos, lead paint, mold, underground storage tanks, wetlands, and endangered species.
Key Features of Environmental Due Diligence
Here are some key features of environmental due diligence:
- Phase I ESA: Historical research, site inspection, and interviews
- Phase II ESA: Soil, groundwater, and air testing (if needed)
- Asbestos, Lead Paint, and Mold Evaluations: Crucial for protecting tenant health and complying with regulations.
- Underground Storage Tank Investigation: Identifying potential leaks and associated costs.
- Wetlands and Endangered Species Assessment: Ensuring compliance with federal and state regulations.
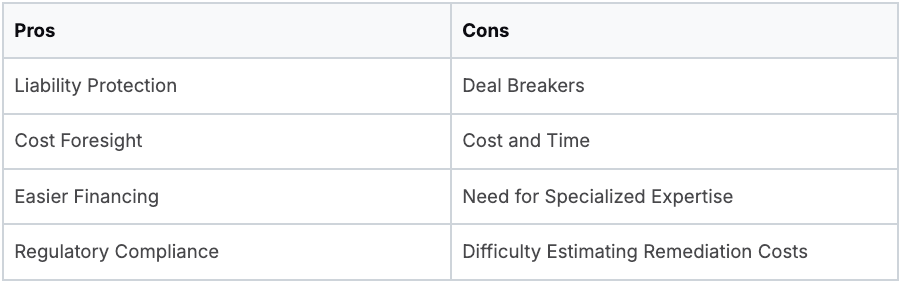
Pros and Cons of Environmental Due Diligence
Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of due diligence is important for informed decision-making.
Real-World Examples of Effective Due Diligence
Here are a couple examples of how environmental due diligence has benefitted real estate companies:
- Simon Property Group: Their standard practice of conducting thorough environmental assessments reportedly avoided a $4.2 million liability. Contamination from a former dry cleaner was discovered at a potential acquisition site.
- Trammell Crow Company: Their successful remediation of a brownfield site in Denver transformed a contaminated industrial property. The site became a thriving mixed-use development, showcasing the potential value of addressing environmental concerns.
Tips for Implementing Environmental Due Diligence
The following tips can help ensure effective due diligence:
- Always Conduct a Phase I ESA: Even if lenders don't require it, it's a critical first step in understanding potential environmental risks.
- Review Prior Reports: Examine existing environmental reports for the property to understand its history.
- Consider Environmental Insurance: For properties with a history of industrial use, environmental insurance can mitigate potential financial risks.
- Understand Regulations: Be familiar with state-specific environmental regulations and cleanup standards.
- Verify Consultant Credentials: Ensure your consultant has appropriate professional liability insurance and relevant experience.
The Importance of Environmental Due Diligence
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), ASTM International (with its E1527 standard for Phase I ESAs), and the Environmental Bankers Association have helped standardize environmental due diligence. Increased awareness of environmental risks and stricter regulations have made this process essential for commercial real estate transactions. By prioritizing environmental due diligence, real estate professionals make informed investment decisions, mitigate risks, and contribute to responsible property development. This proactive approach protects both the investment and the environment.
4. Legal and Title Review
Legal and Title Review is a crucial step in commercial real estate due diligence. It protects your investment by ensuring clear ownership and identifying potential legal issues. This comprehensive examination covers all legal documents and title concerns related to the property. This includes everything from ownership history and easements to zoning compliance and pending litigation. For real estate syndicators, multifamily investors, and sponsors, overlooking this step can lead to costly delays, unforeseen expenses, and even deal-breaking discoveries later on.
The review process involves several key components:
- Title Search and Title Insurance Commitment Review: This confirms the seller's legal right to sell and identifies any liens, encumbrances, or other ownership issues. Reviewing the title insurance commitment is critical, as it outlines coverage and exceptions.
- Survey Analysis (ALTA/NSPS Land Title Survey): An ALTA/NSPS Land Title Survey offers a detailed view of property boundaries, easements, encroachments, and other physical features. It's far more comprehensive than a standard survey and is highly recommended.
- Easement and Encumbrance Evaluation: This involves analyzing any easements (rights of way) or encumbrances (restrictions) on the property. Examples include utility lines, access roads, or conservation restrictions. These can significantly impact future development plans.
- Zoning Compliance Verification: Confirming the property's current use aligns with local zoning regulations is essential. It also involves examining potential future zoning changes that might affect your investment strategy.
- Covenant, Condition, and Restriction (CC&R) Review: For properties with CC&Rs, such as those in a homeowner's association, understanding these restrictions is crucial. They can dictate everything from building appearance to permitted uses.
- Pending Litigation Search: This search reveals any ongoing or past legal disputes involving the property or the seller, potentially impacting ownership or future use.
Pros of a Thorough Legal and Title Review
- Ensures Clear Title and Legal Ownership Transfer: This safeguards your investment by verifying clear ownership and facilitating a smooth transaction.
- Identifies Use Restrictions: Understanding restrictions upfront allows for informed decisions and accurate property valuation.
- Prevents Unexpected Legal Challenges: Addressing potential legal issues during due diligence minimizes the risk of costly surprises after acquisition.
- Uncovers Potential Boundary Disputes: A thorough review can reveal boundary discrepancies or access limitations that could impact future development.
Cons of Legal and Title Review
- Requires Specialized Expertise: Navigating complex legal documents often requires experienced real estate attorneys.
- Can Delay Closing: Addressing complex title issues can be time-consuming and potentially delay the closing process.
- Encumbrances May Be Difficult to Remove: Some encumbrances may be challenging or impossible to remove, impacting the property's value.
- Can Uncover Deal-Breaking Issues Late: Discovering significant legal problems late in due diligence can lead to wasted time and resources.
Real-World Examples
- Prologis: Prologis, a leading logistics real estate company, once uncovered an unrecorded utility easement during due diligence. This would have prevented their planned expansion of a distribution facility. The timely discovery saved them significant time and expense.
- Tishman Speyer: Tishman Speyer, a global real estate development company, routinely performs extensive title research. This averted a major acquisition problem when they found an option agreement granting a neighboring property owner the first right of refusal.
Tips for Effective Legal and Title Review
- Carefully review title commitment exceptions, not just the standard ones.
- Request and review an ALTA/NSPS Land Title Survey instead of relying on existing surveys.
- Obtain zoning verification letters from local authorities.
- Check for pending or proposed zoning changes.
- Research court records for liens and judgments against both the property and the seller.
Organizations like the American Land Title Association (ALTA) and the National Society of Professional Surveyors (NSPS) provide standards and best practices for title review and surveying. Title insurance companies like First American Title Insurance Company and Chicago Title Insurance Company also offer valuable resources and expertise.
Prioritizing Legal and Title Review helps real estate professionals mitigate risk and make informed investment decisions. This crucial due diligence component provides the foundation for a secure and profitable investment.
5. Lease and Tenant Analysis
Lease and tenant analysis is a crucial component of commercial real estate due diligence. It involves a thorough examination of all lease agreements, tenant financials, occupancy history, and the overall tenant mix. This process helps investors understand the quality of their tenants, the security of their leases, potential risks associated with lease expirations (rollover risk), and the likelihood of stable income generation. A robust lease and tenant analysis can significantly impact investment decisions and long-term property performance.
This analysis delves into several key features:
- Lease abstraction and summarization: Condensing complex lease agreements into concise summaries for easier review and comparison.
- Tenant financial strength assessment: Evaluating the financial health of tenants to gauge their ability to meet lease obligations. This might include reviewing credit reports, financial statements, and industry benchmarks.
- Lease expiration schedule and rollover risk analysis: Identifying upcoming lease expirations and assessing the potential impact on occupancy and income. This helps investors proactively manage lease renewals or find replacement tenants.
- Review of tenant improvement allowances and obligations: Understanding the financial responsibilities of both landlord and tenant regarding property improvements.
- Analysis of CAM (Common Area Maintenance) reconciliations: Verifying the accuracy and fairness of CAM charges, ensuring compliance with lease terms.
- Tenant compliance verification: Confirming that tenants are adhering to the terms of their leases, including permitted use, insurance requirements, and other obligations.
Pros of a Thorough Lease and Tenant Analysis
- Identifies tenant default risks and credit concerns: Early identification of potential financial difficulties allows investors to take proactive measures.
- Helps forecast future occupancy and income stability: Understanding lease terms and tenant health provides a clearer picture of future cash flow.
- Reveals lease provisions that could affect property value: Unfavorable lease clauses can negatively impact a property's market value. A detailed analysis helps uncover these potential issues.
- Assists in identifying opportunities for lease restructuring: Analysis may reveal opportunities to renegotiate lease terms and optimize income potential.
Cons of Lease and Tenant Analysis
- Time-consuming to review complex commercial leases: Commercial leases can be lengthy and intricate, requiring significant time and expertise to analyze thoroughly.
- Tenant financial information may be difficult to obtain: Accessing detailed financial information for private companies can be challenging.
- Future tenant performance cannot be guaranteed: While analysis provides insights into current and past performance, it cannot predict future tenant behavior with absolute certainty.
- Lease language can be ambiguous and subject to interpretation: Disputes can arise over the interpretation of specific lease clauses.
Real-World Examples
Brookfield Property Partners, a global real estate investment firm, utilizes proprietary credit scoring models in their tenant analysis for office acquisitions. This approach predicted tenant defaults during the 2020 pandemic with remarkable accuracy (87%). Similarly, Kimco Realty, a major owner and operator of open-air shopping centers, strategically analyzes the health of its anchor tenants. This allows them to proactively address underperforming retailers and secure replacements before lease expirations, minimizing disruption and maintaining occupancy rates.
Tips for Effective Lease and Tenant Analysis
- Request tenant estoppel certificates to verify lease terms and confirm the absence of landlord defaults.
- Create a lease expiration schedule to visualize rollover risk and plan accordingly.
- Analyze tenant improvement expenditures against industry benchmarks to identify potential overspending or inadequate investment.
- Review tenant sales data (if available) to assess location performance and tenant viability.
- Check for co-tenancy clauses that could trigger rent reductions or lease terminations.
- Verify the proper CAM calculation methodology and ensure compliance with lease terms. You might be interested in: Our guide on how to screen tenants for further insights into tenant evaluation.
Organizations such as the International Council of Shopping Centers (ICSC) and the National Association of Industrial and Office Properties (NAIOP) have promoted the importance of thorough lease and tenant analysis. Software solutions like MRI Software (lease administration) and CoStar Group (tenant data and analysis) have also facilitated more efficient and comprehensive reviews. This critical due diligence step deserves its place on the checklist because it directly impacts an investment’s potential for success, helping investors mitigate risks and make informed decisions based on a deep understanding of the property’s income stream and tenant profile.
6. Market and Location Analysis

For real estate professionals like syndicators, multifamily investors, and sponsors, understanding the market and location is crucial. Due diligence goes beyond personal preferences; it demands a thorough evaluation of the property's market standing, competition, local economic trends, and location-specific factors influencing value and performance. This analysis provides essential context for financial projections and investment decisions, making it a cornerstone of any commercial real estate due diligence checklist.
This research helps investors grasp market dynamics, such as supply and demand, and allows for a precise assessment of future growth.
Key Features of Market and Location Analysis
A robust analysis includes several key components:
- Demographic Analysis and Population Trends: Understanding current and projected population growth helps predict future housing and commercial space demand.
- Local Employment and Economic Indicators: Strong employment and positive economic indicators suggest a healthy market, potentially leading to rent growth and property appreciation.
- Competitive Property Analysis: Analyzing comparable properties' rents, occupancy rates, and amenities helps determine competitive pricing and positioning.
- Infrastructure and Transportation Evaluation: Access to highways, public transit, and other infrastructure significantly impacts property value and tenant appeal.
- Development Pipeline Assessment: Understanding planned developments allows for anticipating future competition and potential market shifts.
- Neighborhood and Submarket Analysis: Examining local amenities, crime rates, schools, and other neighborhood characteristics provides a comprehensive view of the investment landscape.
Pros of a Thorough Analysis
Conducting a detailed market and location analysis offers several advantages:
- Context for Financial Projections: Accurate income and expense projections rely heavily on a solid understanding of market dynamics.
- Identifying Emerging Trends: Recognizing growth areas early can lead to higher returns.
- Risk Reduction: A clear understanding of the competitive landscape helps mitigate potential risks.
- Accurate Property Valuation: A comprehensive analysis provides a reliable basis for determining fair market value.
Cons to Consider
While crucial, market and location analysis also has limitations:
- Changing Market Conditions: Unforeseen events can impact market conditions after acquisition.
- Quantifying Qualitative Factors: Aspects like neighborhood appeal can be subjective and difficult to measure.
- Data Availability: Access to reliable data can vary significantly by market.
- Local Expertise: Data interpretation often requires local market knowledge for accurate insights.
Real-World Examples
Hines, a global real estate firm, used in-depth market analysis to identify burgeoning tech corridors in Austin, Texas, before they became widely recognized. This allowed them to acquire properties at attractive prices and capitalize on substantial appreciation. Similarly, Cushman & Wakefield's predictive analytics successfully forecast the post-pandemic suburban office recovery, demonstrating the power of sophisticated market analysis.
Tips for Effective Analysis
Here are some practical tips for conducting a thorough analysis:
- Historical Data: Analyze 5-10 years of historical market data to identify cycles and trends.
- Local Officials: Meet with local economic development officials to gather insights into future plans.
- Property Tours: Tour competitive properties to assess quality and positioning firsthand.
- Multiple Data Sources: Use multiple data sources to verify information and ensure accuracy.
- Location Metrics: Evaluate walk scores, transit scores, and other metrics to quantify accessibility and desirability.
- Future Infrastructure: Consider future infrastructure projects that could impact accessibility and property value.
Key Players and Resources
Organizations like the CoStar Group, CBRE Research, the Urban Land Institute (ULI), and Newmark Knight Frank offer valuable resources and tools for market analysis. Leveraging these resources, along with local expertise, empowers real estate professionals to make informed investment decisions and mitigate potential risks.
7. Insurance and Risk Assessment
Insurance and risk assessment are essential for commercial real estate due diligence. This involves carefully evaluating a property's insurance needs, the effectiveness of current coverage, potential risks, and past claims. This process helps investors understand possible liabilities, budget for insurance costs, and create strategies to protect their investment. For real estate syndicators, multifamily investors, and sponsors, understanding and mitigating risk is crucial for project success.
This goes beyond just verifying the existence of insurance. It means diving deep into the specifics of the coverage, making sure it aligns with the property's unique risks and the investor's strategy. By identifying and quantifying potential risks early on, investors can make informed decisions, negotiate favorable coverage terms, and protect their profits.
Features of a Comprehensive Insurance and Risk Assessment
- Property Insurance Coverage Review: This involves examining existing policies for adequacy in areas like property damage, liability, and business interruption.
- Natural Disaster Risk Assessment: Evaluating the property's vulnerability to floods, earthquakes, wildfires, and other natural hazards. This often includes checking FEMA flood maps and using third-party assessments.
- Loss History Analysis (COPE): Analyzing past claims related to Construction, Occupancy, Protection, and Exposure to understand recurring problems and potential future losses.
- Business Interruption Coverage Evaluation: Determining if the coverage adequately compensates for lost income and expenses during property downtime due to covered events. Realistic restoration timelines are vital for accurate assessments.
- Environmental Liability Insurance Analysis: Assessing potential environmental risks and the need for specialized insurance coverage, often based on Phase I/II Environmental Site Assessments.
- Terrorism Risk Insurance Assessment: Evaluating the potential impact of terrorism and the availability of suitable coverage.
Pros of a Thorough Insurance and Risk Assessment
- Identifies and Quantifies Potential Risk Exposures: This allows for data-driven decisions and informed risk mitigation.
- Accurate Insurance Budgeting: Helps investors avoid unexpected costs and ensures proper financial planning.
- Negotiation Leverage: Provides the information needed to negotiate better coverage terms and premiums with insurers.
- Lender Requirements: Meets lender requirements for insurance coverage, which simplifies loan closing.
Cons of Insurance and Risk Assessment
- Fluctuating Insurance Costs: Premiums can change significantly, affecting projected expenses.
- Uninsurable Risks: Some risks might be difficult or impossible to insure, requiring alternative risk management strategies.
- Specialized Expertise: Complex coverage analysis often requires help from insurance professionals and risk assessors.
- Climate Change Impact: Natural disaster risks are increasing because of climate change, leading to higher premiums and possible coverage limitations.
Real-World Examples of Effective Risk Management
- Vornado Realty Trust: Their due diligence identified insufficient flood coverage before Hurricane Sandy, enabling them to secure more coverage and reduce potential losses.
- Boston Properties: They use a standardized risk assessment protocol that evaluates 42 different risk categories for every acquisition, demonstrating a proactive approach to risk management.
Practical Tips for Implementation
- Professional Loss Control Report: Hire a qualified risk assessor to conduct a property loss control report to identify potential hazards and recommend mitigation measures.
- Flood Zone Verification: Check flood zone designations using FEMA maps and independent assessments.
- Claims History Review: Review the insurance claims history for the past 5 years, at least, to identify recurring problems.
- Parametric Insurance: Consider this type of insurance for catastrophic risks in high-hazard areas; it offers quick payouts based on pre-defined triggers.
- Realistic Restoration Timeframes: Evaluate business interruption coverage based on realistic restoration timelines, factoring in potential supply chain problems and contractor availability.
- Environmental Insurance Needs: Assess environmental insurance needs based on Phase I/II Environmental Site Assessment findings.
Key Players & Organizations
The importance of insurance and risk assessment in commercial real estate is emphasized by organizations like the Risk Management Society (RIMS), and leading insurance brokers and risk consultants like Marsh & McLennan, FM Global, and Aon Risk Solutions. These organizations offer resources, best practices, and specialized expertise in property risk assessment and insurance.
By integrating a thorough insurance and risk assessment into due diligence, real estate investors can significantly lower their risk and make informed decisions to protect their investments. This is a critical step for responsible and successful real estate investing.
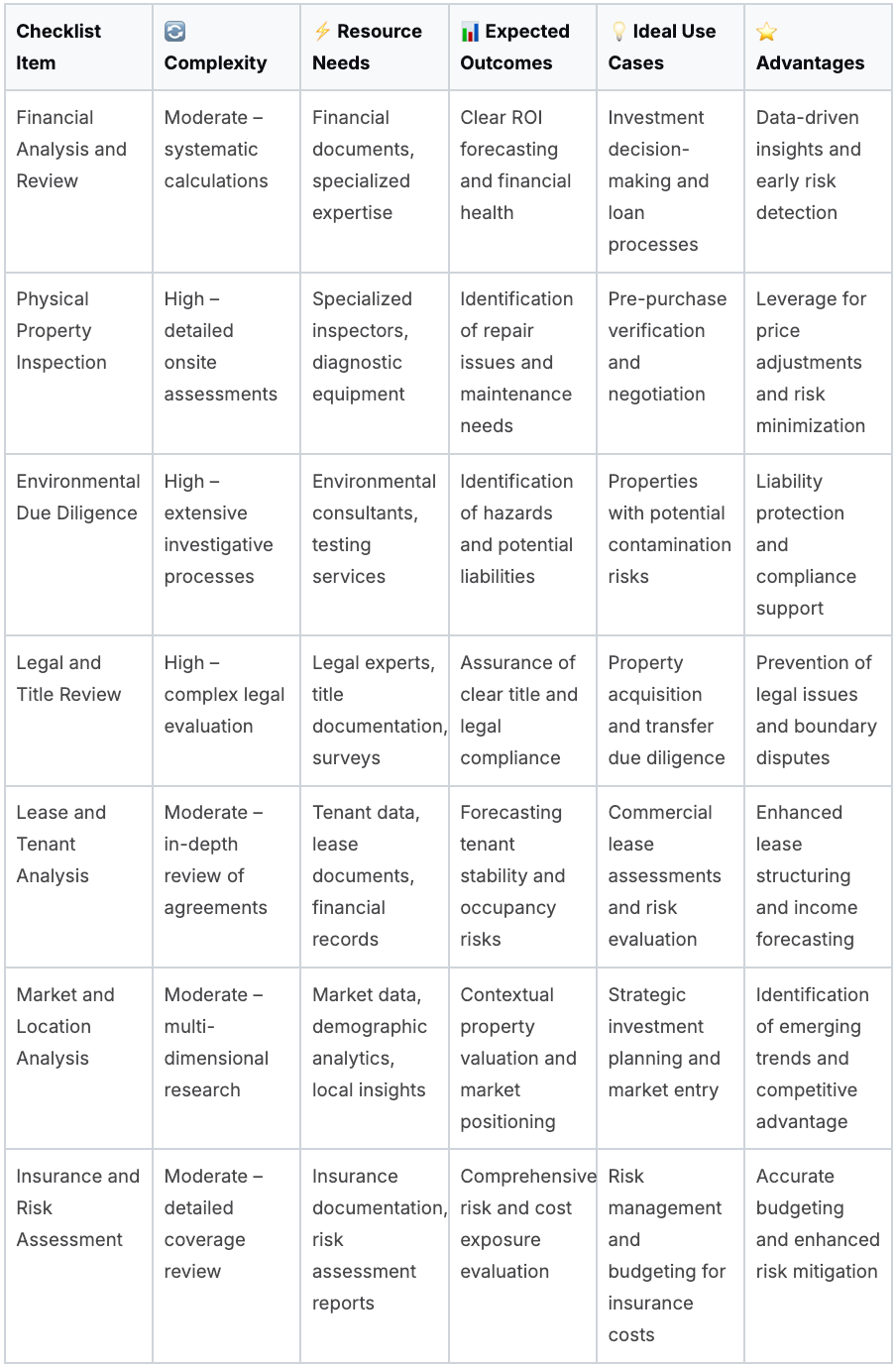
7-Point Comparison: CRE Due Diligence Essentials
Navigating Commercial Real Estate Due Diligence: Your Path To Success
Successfully navigating the complexities of commercial real estate investment requires a thorough and systematic approach to due diligence. From financial analysis and physical inspections to legal reviews and market research, each step in the due diligence checklist plays a vital role in mitigating risk and maximizing potential returns. Applying these concepts effectively requires meticulous planning, detailed record-keeping, and a willingness to adapt your strategy to the specific nuances of each deal.
Due diligence is not a static process. The real estate market is constantly evolving, with ongoing trends and future developments impacting market demand, regulatory requirements, financing options, and technological advancements.
Staying informed about these shifts and incorporating them into your due diligence process is crucial for long-term success. Consulting with experienced professionals, such as attorneys, accountants, and environmental consultants, can provide invaluable insights and ensure you're addressing all critical aspects of a potential investment.
Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive Analysis: Due diligence encompasses a wide range of factors, including financial performance, physical condition, legal compliance, market dynamics, and risk assessment.
- Risk Mitigation: A robust due diligence process is essential for identifying potential red flags and minimizing investment risks.
- Informed Decision-Making: Thorough due diligence empowers you to make data-driven decisions and optimize your investment strategy.
- Adaptability: The real estate market is constantly in flux, requiring a flexible and adaptable approach to due diligence.
- Expert Guidance: Seeking professional advice from experienced advisors is crucial for navigating complex transactions and ensuring compliance.
Streamlining your due diligence process and efficiently managing the complexities of real estate syndication can be challenging. That's where Homebase comes in. Homebase is an all-in-one platform designed to simplify fundraising, investor relations, and deal management for real estate operators.
From automated fundraising workflows and KYC/AML verification to secure document sharing and integrated reporting, Homebase provides the tools you need to manage your deals effectively and efficiently. Focus on growing your portfolio, not managing spreadsheets. Visit Homebase today and discover how they can help you scale your real estate syndication business with their flat fee of $250/month for unlimited deals and investors.
Share On Linkedin
Share On Twitter
Share On Linkedin
Share On Twitter
DOMINGO VALADEZ is the co-founder at Homebase and a former product strategy manager at Google.
What To Read Next
A Guide to Real Estate Financial Modelling for Syndicators
Blog
Master real estate financial modelling with this guide. Learn to build models that analyze deals, forecast returns, and build unwavering investor confidence.
Sign up for the newsletter
If you want relevant updates from our team at Homebase, sign up! Your email is never shared.
Sign up for the newsletter
If you want relevant updates from our team at Homebase, sign up! Your email is never shared.
© 2026 Homebase. All rights reserved.