What Is Market Rent? Your Complete Guide to Fair Pricing
What Is Market Rent? Your Complete Guide to Fair Pricing
Discover what is market rent, how it's calculated, and proven strategies for tenants and landlords to navigate rental pricing confidently.
Domingo Valadez
Jun 1, 2025
Blog
Understanding What Market Rent Really Means

Let's clarify market rent. It's the price a property could realistically command in a competitive rental market. It's driven by supply and demand. Similar properties in the same area will typically rent for around the same price, creating a benchmark. This benchmark is crucial for both tenants and landlords.
How Market Rent Differs From Other Rental Prices
Understanding market rent helps you recognize a fair price. It's important to distinguish it from other rental pricing types. Asking rent is the initial advertised price, but it doesn't always reflect true market rent. Negotiation, seasonal changes, or unique property features can influence the final price.
Contract rent is the price locked in through a lease. This can differ from market rent, especially with longer leases signed under different market conditions. This becomes clear if market prices shift significantly during the lease term.
Another difference is between market rent and rent-controlled properties. Regulations in some areas limit rent increases, resulting in contract rent potentially being much lower than market rent. This protects tenants from sharp rent hikes, but can lead to below-market rents in those areas. Understanding local regulations is crucial for assessing a rental price's market accuracy.
Defining Market Value in a Competitive Rental Market
Market rent reflects the prevailing rental price achievable in an open and competitive market, driven by supply and demand without regulatory limitations. By the end of 2024, the national median rent in the United States was approximately $1,373. This represented a 0.6% decrease from the previous month but was still $225 higher than January 2021 levels. For further insights, see Rental Market Trends. However, even within a city, this median rent can vary significantly.
Factors Influencing Market Rent
Several factors determine market rent. Location is key – proximity to amenities, transportation, and good schools significantly impacts prices. Property features, like size, age, amenities, and parking, also matter. A renovated apartment with modern appliances will likely command higher rent than a comparable older unit.
Market conditions, including the local job market, population growth, and economic health, also play a role. A strong job market with high housing demand can push rents up, while economic downturns may lower them. Understanding these dynamics helps evaluate rental price fairness.
Practical Applications of Market Rent Knowledge
Understanding market rent empowers both tenants and landlords. Tenants can negotiate lease terms effectively and avoid overpaying. Landlords can optimize pricing strategies to attract tenants and maximize returns. Ultimately, this knowledge facilitates smarter decisions for everyone in the rental market.
The Hidden Forces That Set Your Rent Price

Why does the same apartment type cost different amounts just blocks away? This section reveals the forces behind market rent, the price tenants actually pay for comparable properties in a competitive market. Understanding these factors helps you make informed decisions, whether you're renting or investing.
External Market Dynamics: Beyond the Building
Market rent isn't solely determined by the property itself. External factors play a significant role, much like pricing any other product. Broader market conditions always influence cost.
A thriving local job market, for instance, often increases demand for housing, driving rents upward. Conversely, economic downturns can soften demand and potentially lower market rent.
Population trends also affect rental prices. Rapid population growth in an area with limited housing can lead to higher rents. Therefore, understanding the demographics of your target area is crucial.
Property Characteristics: Location, Amenities, and More
While external forces set the overall market tone, individual property characteristics create pricing tiers within a neighborhood. Location is key.
An apartment on a bustling street with easy access to shops and public transport will likely command a higher market rent. This contrasts with a similar unit located further away from these conveniences.
Building age and amenities also influence pricing. Newer constructions with updated appliances, in-unit laundry, and amenities like fitness centers often justify higher rents. Features like off-street parking or pet-friendly policies can also increase market rent.
Interest Rates and Housing Inventory
The real estate market operates within larger economic systems. Fluctuations in interest rates impact affordability for both renters and buyers. Higher interest rates can cool down the buying market, leading to increased rental demand and higher market rents.
Lower interest rates can make homeownership more attractive. This potentially eases rental demand and stabilizes, or even lowers, rental prices.
Local regulations also shape market rent. Rent control policies in some areas can limit rent increases, creating a unique market dynamic. In these cases, contract rent might be significantly below market value. Understanding these regulations is crucial for predicting rent trends.
This combination of external market dynamics and property-specific attributes creates a complex system that determines market rent. Deciphering this system will help you negotiate effectively and make informed rental choices.
Coast-to-Coast Market Rent Reality Check
Understanding market rent is crucial for both tenants and landlords. Regional variation significantly impacts rental prices. Market rent reflects economic opportunity and disparity across the US. Why the dramatic price differences between cities? Examining economic forces helps explain these variations.
This infographic visualizes how rent is calculated, considering factors like location and property features. The calculator and documents illustrate how different elements contribute to determining market rent. This emphasizes that market rent is a calculated value, not an arbitrary number.
Major Metropolitan Areas vs. Smaller Markets: Unpacking the Price Gap
Comparing major metropolitan areas with smaller markets reveals the reasons behind pricing differences. Bustling cities like New York and San Francisco, with high population density and strong job markets, often have higher market rents due to increased demand and limited housing supply.
Smaller markets or cities with less robust economies may have lower rent due to reduced demand. Location dramatically impacts what tenants pay monthly. Median rental prices vary significantly. New York averages $4,300 per month, Boston around $3,874, and Jersey City $3,090. More affordable states like West Virginia have median rents as low as $927, while South Dakota and Arkansas are just above $1,090. Resimpli provides more detailed rental market statistics. Researching specific locations is essential to understanding fair market value.
To further illustrate these regional variations, let's examine a comparison table:
This table compares average market rents across several US locations, highlighting the differences between high-cost and more affordable markets. It also explores some key factors influencing these price disparities.
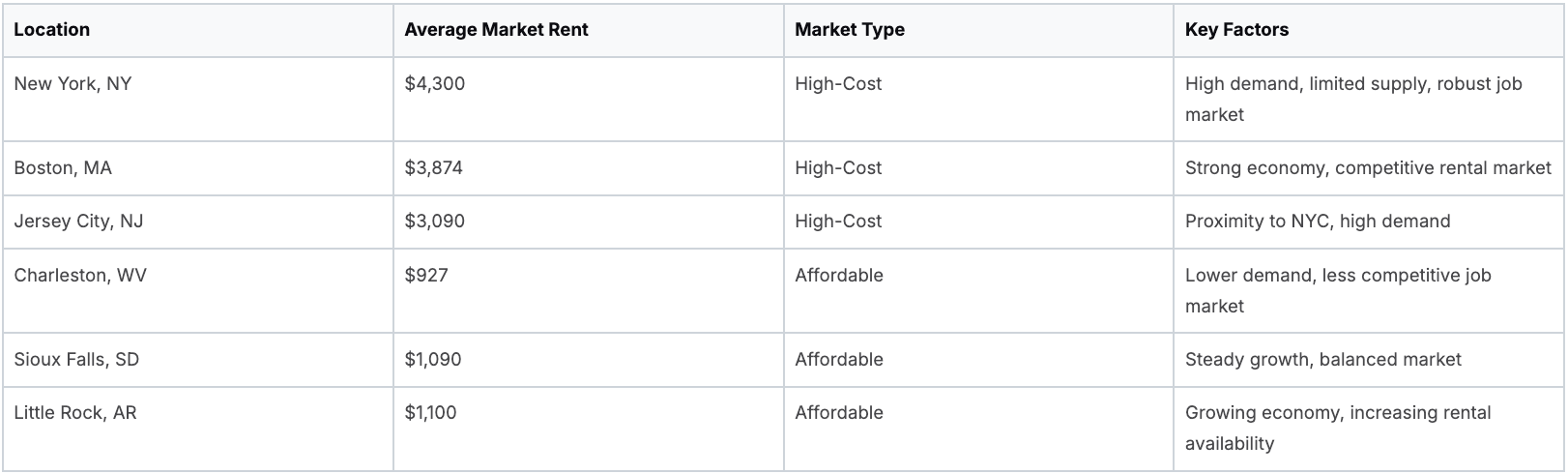
As you can see, the average market rent varies greatly depending on location, influenced by factors like job market strength and housing supply and demand dynamics.
Regional Variations: Beyond the City Limits
Beyond the city-versus-small-town comparison, other regional factors influence rent. Job availability, population density, and local housing policies contribute to price fluctuations. Areas with high job growth and limited housing see escalating rents.
Local housing policies, such as rent control, can also influence prices. These regulations can create situations where contract rent is significantly below market value. Understanding these local nuances is critical when evaluating rentals. This knowledge helps individuals assess if relocating for better rental value aligns with their financial goals and lifestyle.
Practical Strategies: Finding the Best Deals
Market knowledge is key to finding the best rental deals. By researching comparable properties and understanding the factors influencing rent, tenants can negotiate lease terms and secure favorable pricing. This allows tenants to determine if a property is fairly priced or if there's room for negotiation. This empowered approach can save a substantial amount of money over a lease term.
The Trillion-Dollar Shift Toward Renting
Renting is transforming the housing landscape, evolving from a short-term solution to a major economic force. It's not just about temporary accommodations anymore; it's influencing investment decisions and shaping long-term lifestyle choices. Let's examine the remarkable growth of the rental market and explore how tenant expectations and landlord strategies are changing.
The Expanding Rental Market: A Global Overview
The rental market's growth is truly impressive. This expansion demonstrates a global trend toward renting as a preferred housing option. In 2024, the global real estate rental market reached approximately $2.69 trillion and is projected to reach $2.91 trillion in 2025. This signifies a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.2%. For a more detailed analysis of these market dynamics, you can find more detailed statistics here. This growth highlights the increasing significance of renting in the worldwide economy.
Evolving Consumer Preferences: What Renters Seek
Several key factors are driving this shift. The rise of remote work has lessened the need to live near traditional office hubs, offering renters greater flexibility in location. Additionally, increasing housing costs in many urban centers make renting more financially viable than buying, particularly for younger demographics.
Sustainability is also a growing concern influencing housing decisions. Renters are increasingly interested in properties with eco-friendly features and a reduced environmental footprint. These evolving preferences are redefining what constitutes an attractive rental property.
Market Rent in a Dynamic Environment: Adapting to Change
These overarching trends are impacting how market rent is established. Heightened demand in specific locations, combined with desirable amenities and features, can significantly influence rental prices. Landlords are adapting by incorporating sought-after amenities and adjusting their pricing strategies to stay competitive.
For instance, properties offering co-working spaces, pet-friendly accommodations, and sustainable features may command higher market rents. Understanding these evolving trends is vital for both renters and landlords.
Utilizing Market Insights for Success
Savvy renters and property owners are already capitalizing on these market shifts. Renters can use market knowledge to find the best value and negotiate favorable lease terms. Landlords can adapt their properties and pricing to attract and retain tenants, maximizing their return on investment.
A thorough understanding of market rent empowers both parties to make informed decisions in today's dynamic rental market. This knowledge is essential for navigating the modern rental landscape.
When Rising Rents Meet Reality
Let's face it: rental costs are increasing worldwide, impacting renters everywhere. This begs the question: why are rents rising, and what does it mean for renters trying to understand market rent?
The Sobering Data Behind Rising Rents
Understanding market rent means acknowledging the current rental landscape. Data shows a significant jump in rental costs. Renters are spending nearly 18% more on rent compared to January 2023, as of November 2024. Several factors drive this increase, including inflation, housing shortages, and high demand, especially in major cities. Learn more about these trends at Rent Has Increased Around the Globe - What To Expect In 2025. This sharp rise underscores the importance of understanding what drives market rent.
Why Rents Keep Climbing
Several factors contribute to rent increases. Inflation plays a key role, as rising costs of goods and services extend to housing. This means landlords face increased operating expenses, often passed on to tenants as higher rents. Limited rental availability, particularly in desirable locations, also fuels the rise. This housing shortage creates competition, allowing landlords to charge more.
The Impact on Household Budgets
Escalating rental costs have significant consequences for household budgets. Higher rents force renters to allocate more income to housing, leaving less for other necessities. This financial strain can lead to difficult choices and highlights the importance of understanding market rent when looking for a place to live.
Emerging Trends in the Rental Market
The challenges of rising rents have led to new trends. Longer lease terms are becoming common as both tenants and landlords seek stability. Renters lock in a set price, while landlords secure guaranteed income. Tenant preferences for amenities are also evolving. While some amenities remain popular, others are less important as affordability takes priority. These changes influence how market rent is determined.
Navigating the Challenging Landscape
Navigating today's rental market requires a proactive, informed approach. Understanding how market rent is calculated and influenced by market forces is crucial. Researching different neighborhoods and considering various rental options is beneficial. This includes exploring alternatives like co-living or shared housing to manage costs.
Identifying Value Opportunities
Even in expensive markets, value can be found. By focusing on needs and prioritizing essential features over luxury extras, renters can find affordable options. Negotiating with landlords and being flexible with move-in dates can also yield positive results. This allows tenants to find housing within their budget that aligns with their needs and lifestyle.
Your Market Rent Research Toolkit
Understanding market rent is crucial for both tenants and landlords. It's more than just knowing the definition; it's about having the tools and strategies to find accurate, real-time data. This section will equip you with actionable techniques to investigate rental prices in your area, empowering you to make well-informed decisions.
Online Resources: Your Starting Point
The internet offers a wealth of information for researching market rent. Popular real estate portals like Zillow, Apartments.com, and Trulia provide listings with rental prices, often including historical data and trends. These platforms offer a user-friendly way to get a quick snapshot of current market conditions.
However, relying solely on these sites isn't enough. Their data isn't always completely up-to-date and can be influenced by listing inaccuracies. Cross-referencing information from multiple sources is key.
- Zillow: Offers extensive rental listings, historical data, and valuable neighborhood information.
- Apartments.com: Specializes in apartment rentals and provides detailed search filters to refine your search.
- Trulia: Offers similar features to Zillow, with a particular focus on community insights.
Local Data Sources: Deeper Dive
For a more accurate understanding of the market, explore local resources. Local newspapers, community forums, and real estate agent websites can provide more granular insights into specific neighborhoods and rental trends.
Consider contacting local property management companies for their perspectives on current market rates. This direct approach can offer invaluable, first-hand information.
Analyzing Comparable Properties: Apples to Apples
One of the most effective research strategies is analyzing comparable properties, often called "comps." Find similar rentals in the same area, considering factors like size, age, amenities, and location.
Comparing these "apples-to-apples" rentals gives you a realistic range for market rent. This method mirrors how real estate investors evaluate potential deals, as detailed in our guide on How to Analyze Real Estate Deals.
Hidden Costs and Total Housing Expenses
Don't just focus on the base rent. Factor in additional expenses like utilities, parking, pet fees, and renter's insurance. These hidden costs can significantly impact your total housing expenses. Accurately assessing these will provide a more complete picture of affordability.
Timing Your Research: Seasonal Advantage
Rental markets fluctuate seasonally. Demand, and therefore prices, are typically higher during peak seasons, such as summer. Researching during the off-season can uncover better deals and give you greater negotiating power. Understanding these seasonal patterns can give you a distinct advantage.
The following table summarizes some key tools and resources you can use for your market rent research. It highlights the benefits and drawbacks of each approach, giving you a comprehensive overview to inform your strategy.
Market Rent Research Tools and Resources: Essential tools and platforms for researching accurate market rent data, with pros and cons of each approach
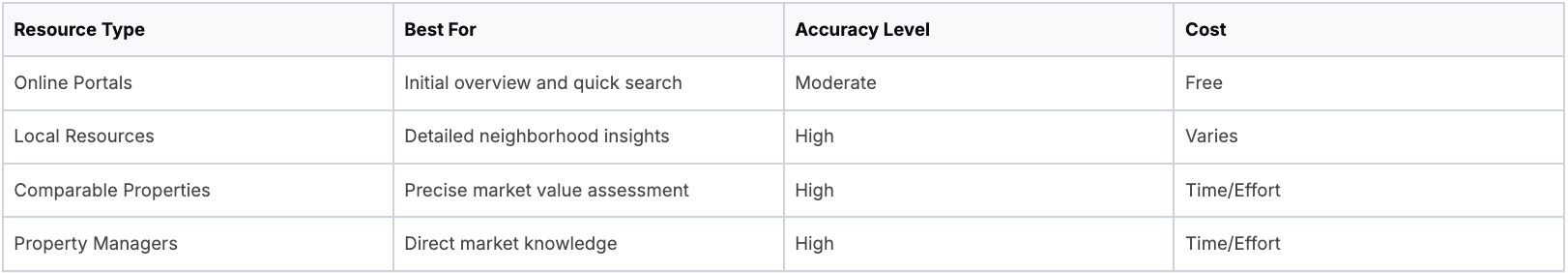
By utilizing these research tools and understanding the various factors that influence rental prices, you can confidently navigate the rental market. Make informed decisions that align with your budget and housing needs.
Making Smart Moves With Market Rent Intelligence
Understanding market rent is crucial for navigating the rental landscape. This section offers practical strategies for evaluating rental opportunities, timing your search, and negotiating effectively, regardless of whether you're a tenant or a landlord.
Evaluating Rental Opportunities: Is It a Good Deal?
Market rent data empowers you to assess the true value of a rental. Compare the asking rent to the market rent for similar properties in the area. If the asking rent is significantly higher, it might be overpriced. Conversely, a rent below market value could signal a great deal or potential hidden problems.
For example, imagine you're looking at a two-bedroom apartment with a $1,800 asking rent. Your research reveals similar units rent for around $1,600. This difference suggests the property might be overpriced. However, unique amenities or recent renovations could justify the higher price. Careful evaluation is key.
Timing Your Search: The Seasonal Advantage
The rental market, like other markets, experiences seasonal fluctuations. Demand, and consequently prices, typically rise during peak seasons. This often coincides with increased moving activity, such as the summer months or the start of a school year.
Searching during the off-season can often yield better deals. Landlords may be more willing to negotiate on price or offer incentives to fill vacancies during slower periods. Using this seasonal knowledge can give you an advantage.
Negotiation Tactics: Getting the Best Terms
Whether you are a tenant or a landlord, understanding market rent is essential for successful negotiation. Tenants can use market data to justify requests for lower rent or other concessions. Landlords can use it to confidently support their pricing.
- For Tenants: Researching comparable properties provides leverage when negotiating.
- For Landlords: Market rent data helps justify pricing and demonstrate fairness.
Focusing on a longer lease term can benefit both parties. Tenants secure a fixed price, providing budget predictability. Landlords secure guaranteed income for an extended period, creating a mutually beneficial agreement.
Long-Term Planning: Beyond the Lease
Market rent data isn't just for immediate decisions; it's vital for long-term planning. As a tenant, consider future rent increases and their impact on your budget. As a landlord, analyze market trends to inform your long-term rental pricing strategy.
This includes considering long-term investment goals and forecasting potential rental income growth. By factoring in market dynamics and future projections, you can make informed decisions about your long-term housing strategy.
Ready to streamline your real estate syndication and optimize your investment strategies? Homebase offers an all-in-one platform for managing deals, investors, and fundraising. Learn how Homebase can simplify your real estate operations and help you achieve your investment goals. Visit Homebase today.
Share On Linkedin
Share On Twitter
Share On Linkedin
Share On Twitter
DOMINGO VALADEZ is the co-founder at Homebase and a former product strategy manager at Google.
What To Read Next
A Guide to Real Estate Financial Modelling for Syndicators
Blog
Master real estate financial modelling with this guide. Learn to build models that analyze deals, forecast returns, and build unwavering investor confidence.
Sign up for the newsletter
If you want relevant updates from our team at Homebase, sign up! Your email is never shared.
Sign up for the newsletter
If you want relevant updates from our team at Homebase, sign up! Your email is never shared.
© 2026 Homebase. All rights reserved.