Syndication Definition in Real Estate: Investors' Guide
Syndication Definition in Real Estate: Investors' Guide
Learn the syndication definition in real estate and unlock powerful investing insights. Click for your guide!
Domingo Valadez
May 7, 2025
Blog
Demystifying Real Estate Syndication: The Essentials

Understanding real estate syndication is key for investors aiming to grow their portfolios. Essentially, it's a collaborative strategy where individuals pool resources to invest in larger real estate projects. This joint effort unlocks opportunities that might be out of reach individually. Think of it like teaming up with friends to buy a vacation property you couldn't afford on your own – everyone contributes, and everyone benefits.
Real estate syndication allows multiple investors to combine funds and acquire a property too expensive for a single buyer. This opens up access to larger investments, like commercial buildings or apartment complexes. Syndications are usually structured as Limited Partnerships (LPs) or Limited Liability Companies (LLCs), offering investors liability protection. A sponsor, typically a real estate professional, manages the property and receives a larger share of the profits. Passive investors earn returns based on their investment.
A sponsor might invest 5% to 15% of the equity, with investors contributing the remaining 85% to 95%. This setup lets investors benefit from real estate without daily management responsibilities. Learn more about real estate syndication at CaliberCo.
Breaking Down the Benefits
This collaborative approach offers several advantages. It lowers the financial hurdle for individuals, making larger, potentially more lucrative projects achievable. It also diversifies risk. Instead of concentrating capital in one project, you spread it across multiple properties, reducing the impact of any single investment's underperformance.
Understanding the Key Players
Two main roles exist in real estate syndication: the sponsor and the investors. The sponsor, also known as the syndicator, is the project's driving force. They identify opportunities, secure financing, manage the property, and oversee the investment strategy. They essentially act as the project manager.
Investors provide the capital. They are typically passive, not involved in daily property management. They benefit from the sponsor's expertise and share in the profits. They act like silent partners, contributing financially and sharing in the rewards. This partnership between sponsor and investor is the core of real estate syndication, allowing both parties to achieve their investment objectives.
The Syndication Dream Team: Who Does What

Behind every successful real estate syndication, a dedicated team collaborates to achieve a shared investment objective. This cooperative approach, fundamental to real estate syndication, hinges on each member fulfilling their role effectively. This section outlines the key responsibilities within a typical real estate syndication structure.
The Sponsor: Spearheading the Project
The sponsor, also known as the syndicator, acts as the project's leader. They are responsible for identifying and acquiring suitable investment properties, performing thorough due diligence, obtaining necessary financing, and overseeing the property's management. They essentially function as the project's CEO, making crucial decisions and propelling the investment forward. The sponsor's experience and expertise are paramount to the syndication's success.
The following table outlines the key roles and responsibilities within a typical real estate syndication.
Key Roles in Real Estate Syndication
This table outlines the primary responsibilities and typical contributions of the main participants in a real estate syndication deal.
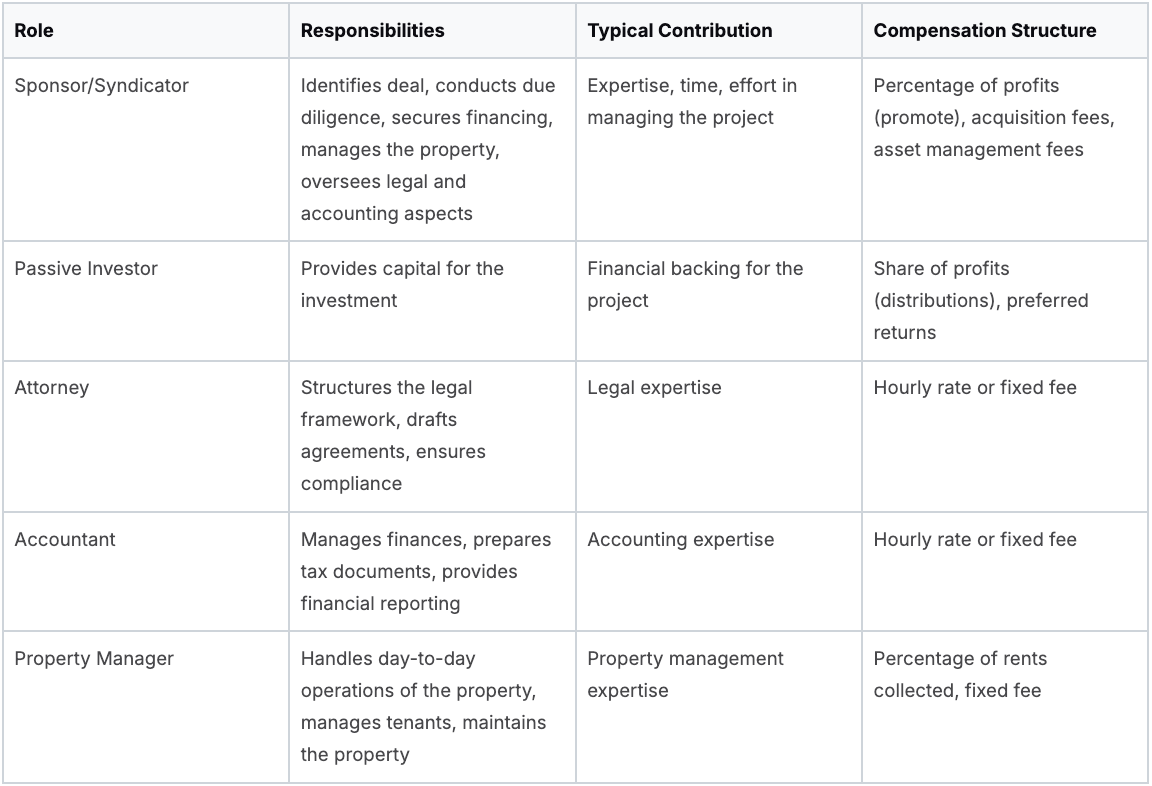
This table highlights the interconnectedness of each role and the distinct contributions each party makes to a successful syndication. Each participant's specialized knowledge and responsibilities are crucial for maximizing the investment's potential.
Passive Investors: Funding the Venture
Passive investors are the financial foundation of the syndication. They provide the necessary capital for acquiring and managing the property. This allows them to invest in large-scale real estate ventures without the demands of active management. Passive investors profit from the property's appreciation and rental income, reaping returns without daily operational involvement.
The Supporting Cast: Facilitating Seamless Operations
Other professionals play vital supporting roles. Attorneys ensure the legal structure and documentation are sound, protecting all parties involved. Accountants manage the financial aspects of the project, delivering precise reporting and offering tax guidance. Property managers handle the daily operations of the property, optimizing its value and ensuring tenant satisfaction.
Evaluating Potential Opportunities
Before investing in a real estate syndication, it's essential to ask critical questions. What is the sponsor's track record and experience? What are the projected returns, associated fees, and the syndication's legal structure? Understanding these aspects will help you make informed investment decisions. Resources like those offered by Homebase can provide further insights into evaluating sponsors and deals. This due diligence is an indispensable step in successful syndication investing.
Legal Frameworks That Protect Your Investment

The legal structure behind a real estate syndication is fundamental to investor protection. It's more than just paperwork; it's the foundation upon which investor safeguards are built. Understanding the definition of a real estate syndication includes grasping these legal nuances. This means knowing how these frameworks protect your investment and what to watch for when evaluating potential opportunities. This knowledge helps empower you to make sound decisions and mitigate potential risks.
Limited Partnerships (LPs) and Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
Two common structures in real estate syndication are Limited Partnerships (LPs) and Limited Liability Companies (LLCs). Each offers distinct advantages and disadvantages regarding liability and taxation. LPs involve general partners, who manage the investment and assume full liability, and limited partners, passive investors with limited liability. LLCs, on the other hand, offer all members limited liability, creating a flexible structure for managing the investment.
For example, consider a syndication investing in a multifamily property. If structured as an LP, the sponsor would likely be the general partner, responsible for the property's management and associated liabilities. The passive investors would be limited partners, their liability limited to their invested amount. If the same syndication were structured as an LLC, all members would benefit from limited liability.
Operating Agreements: Your Roadmap for Success
The operating agreement is a crucial document that governs the syndication. It outlines the rights and responsibilities of all involved parties, the distribution of profits and losses, and the rules for managing and eventually dissolving the syndication. It's essentially the constitution of the investment, dictating how decisions are made and how the venture functions.
Carefully review this document. Look for potential issues, such as excessive fees benefiting the sponsor, unclear exit strategies, or vague decision-making processes. A well-written operating agreement provides transparency and protects your interests throughout the investment's lifecycle.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring Legitimacy
Regulatory compliance is essential in real estate syndication. Securities laws govern these investments, mandating specific disclosures and adherence to regulations. This protects investors from fraudulent or misleading practices and ensures the offering is legitimate. Due diligence in this area is critical.
This involves verifying the sponsor's compliance with securities regulations, confirming the offering is correctly registered (if necessary), and understanding the legal framework governing the investment. This protects you from problematic ventures and safeguards your investment capital.
Aligning Structure with Investment Goals
Different legal structures are better suited for various investment goals. For instance, a fix-and-flip project might benefit from the flexibility of an LLC, while a long-term hold might be better structured as an LP. Aligning the legal structure with your specific investment objectives is crucial for maximizing returns and effectively managing risk. Choosing the appropriate structure helps optimize the investment and provides a clear path toward your financial goals. Platforms like Homebase offer resources and tools to help you navigate these complexities and make educated decisions about real estate syndication. Explore these tools to deepen your understanding and learn more about syndication on Homebase. This knowledge will enable you to make informed decisions and navigate the legal intricacies of real estate syndication.
The Evolution: From Country Club Deals to Crowdfunding

Real estate syndication has dramatically changed. Once the exclusive realm of high-net-worth individuals and country clubs, it now offers opportunities to a much wider range of investors. This evolution is largely due to technological advancements and regulatory changes, broadening the syndication definition in real estate.
The Rise of Crowdfunding
The rise of crowdfunding platforms within the real estate sector is a direct result of this evolution. This innovative approach allows more individuals to participate in larger real estate projects, redefining what's possible for individual investors. Crowdfunding simplifies entry into real estate syndication, lowering the barriers to entry for many.
Platforms like Fundrise and Realty Mogul facilitate this new accessibility. They allow investors to pool their money for large-scale real estate projects, much like traditional syndications but with the added convenience of online participation. This has effectively revitalized public syndication, which was significantly restricted by the Securities Act of 1933. Many crowdfunding platforms often require investors to be accredited to comply with federal securities laws. Fundrise, for example, has opened doors for thousands of investors to participate in projects previously beyond their individual reach, democratizing real estate investing. Learn more about real estate syndication at Commercial Real Estate Loans.
Traditional vs. Crowdfunded Syndications: A Comparison
Both traditional and crowdfunded syndications operate on the core principle of pooling resources. However, key differences exist that significantly impact investor experience, access, and potential returns. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making informed investment decisions.

This table summarizes the key distinctions between these two approaches, catering to different investor profiles and financial goals.
The Future of Real Estate Investing
The evolution of real estate syndication signifies a shift toward greater accessibility and transparency. This empowers individuals to participate in larger ventures and potentially diversify their portfolios. However, it’s essential to carefully consider the risks and rewards associated with each model.
Savvy investors are increasingly using both traditional and crowdfunded syndications for a more diversified real estate portfolio. This blended approach offers the potential to maximize returns while mitigating risks. The future of real estate investing lies in strategically utilizing these evolving opportunities. Platforms like Homebase provide valuable tools and resources to help investors navigate the complexities of real estate syndication and make informed decisions.
The Money Timeline: Entry to Exit Strategies
Understanding the financial lifecycle of a real estate syndication is crucial for potential investors. This involves knowing the various stages of the investment, from the initial capital contribution to the final payout, and when to expect returns. This section explores the timeline of a typical real estate syndication and clarifies the syndication definition in real estate.
From Capital Calls to Distributions: Tracing the Investment Journey
The process begins with a capital call, where investors contribute their agreed-upon funds. This capital is used to acquire the property and cover initial expenses. After the acquisition, the property enters the operational phase. During this time, the sponsor manages the property according to the business plan, aiming to generate income and increase property value.
Regular communication from the sponsor is essential throughout this phase. Investors should receive updates on the property's performance, market conditions, and any significant events. Transparency is key to building trust and a strong sponsor-investor relationship.
You might be interested in: How to master a real estate syndication calculator.
Holding Periods and Exit Strategies: Understanding Your Investment Horizon
The typical holding period for a real estate syndication varies depending on the investment strategy and property type. The investment period generally ranges from three to five years. This is shorter than real estate funds, which can span seven to ten years. Syndications allow investors to closely vet the property and sponsor, providing more control over investment decisions than funds, which often invest in multiple unidentified properties. For example, a syndication might renovate and sell a single apartment complex within three years, offering a clear exit strategy and potential for returns. Learn more about real estate syndication timelines here.
Exit strategies can include refinancing, selling the property, or a combination of both. The chosen strategy impacts the timing and amount of investor returns. A well-defined exit strategy is crucial for a successful syndication.
Realistic Projections vs. Overly Optimistic Promises: A Critical Assessment
It's critical to distinguish realistic projections from overly optimistic promises when evaluating a real estate syndication. While high returns are attractive, it's important to ensure projections are based on solid market analysis and a well-defined business plan. Carefully examine the sponsor's track record, experience, and the assumptions behind their financial forecasts.
Comparing Syndications to Other Investments
How do real estate syndications compare to other investment vehicles? The table below, "Syndication vs. Other Real Estate Investments," highlights the key differences between syndications and alternative investment approaches.
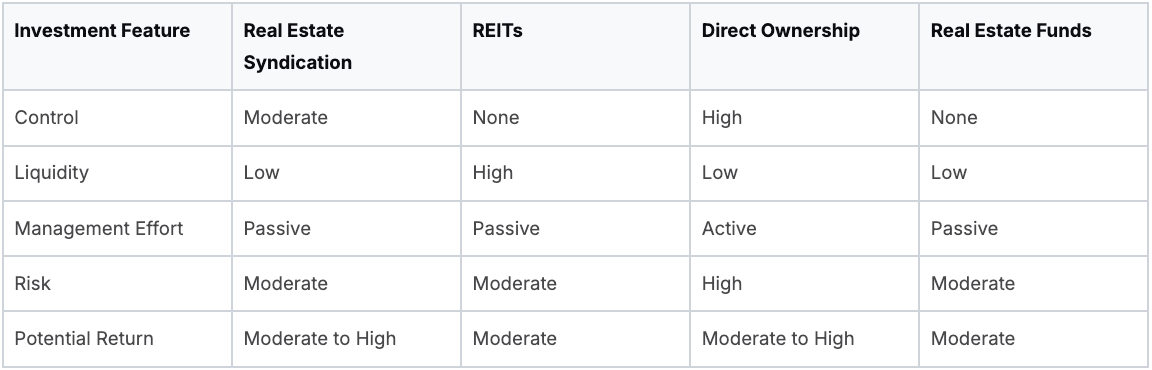
This table shows the trade-offs between different real estate investment options. Syndications offer a balance of control, effort, and potential returns, making them appealing to many investors.
By understanding the money timeline, holding periods, exit strategies, and potential pitfalls, you can make informed decisions about real estate syndication investments. This knowledge will help you evaluate opportunities and choose investments aligned with your financial goals.
Separating Winners From Losers: Due Diligence Mastery
Thorough due diligence is paramount when considering a real estate syndication. Not all opportunities are created equal. The ability to distinguish between promising ventures and potential pitfalls can significantly impact your financial future. Truly understanding the syndication definition in real estate goes beyond the basics. It requires carefully scrutinizing potential deals. This section outlines a systematic framework employed by experienced investors before committing capital.
Deciphering The Offering Memorandum
The offering memorandum is your primary source of information about the syndication. It details the investment strategy, property information, financial projections, and the sponsor's background. Look for clearly articulated investment objectives, a comprehensive market analysis, and realistic financial projections. Carefully examine the sponsor's experience, track record, and any potential conflicts of interest. This document provides a crucial first impression and sets the stage for deeper investigation.
Key Metrics: Red Flags And Green Lights
Certain metrics can signal potential future performance issues. A high loan-to-value ratio (LTV) could indicate excessive debt and increased risk. Unrealistic rent growth projections or inflated occupancy assumptions can lead to disappointing returns. Complex fee structures that disproportionately favor the sponsor also warrant close examination. These financial details can reveal underlying weaknesses or hidden advantages.
Positive indicators, on the other hand, like a strong debt service coverage ratio (DSCR), reasonable expense ratios, and conservative financial projections suggest a well-structured and potentially profitable deal. Identifying these signals helps separate strong investments from weaker ones.
Asking The Tough Questions
Don't hesitate to ask the sponsor challenging questions. Inquire about their experience with similar projects, their risk mitigation strategies, and their exit strategy. How do they plan to handle unexpected challenges like rising interest rates or a downturn in the local market? Thoughtful questions can uncover valuable insights and assess the sponsor’s preparedness. This process also helps build trust and ensures alignment between your investment goals and the syndication’s objectives.
Evaluating The Market: Beyond The Hype
A robust market analysis is essential. Don't be swayed by glossy marketing materials. Look for evidence of thorough research, including an understanding of local market dynamics, demographic trends, and potential competition. Consider how the property’s location compares to similar properties in the area. Is the market experiencing growth, or is it saturated? A thorough market analysis forms the foundation of a sound investment strategy.
Unraveling Fee Structures: Aligning Incentives
Pay close attention to the fee structure. Excessive fees, unclear profit splits, or hidden costs can significantly erode your returns. Look for a fair and transparent fee structure that aligns the sponsor’s incentives with the investors’ interests. This ensures everyone is working towards a shared objective.
Learning From Experience: Successes And Failures
Studying both successful and failed syndications offers valuable lessons. Analyze case studies to understand the factors that contributed to each outcome. This historical perspective can help you identify potential red flags and make more informed investment decisions. Understanding past mistakes can also enhance your ability to anticipate potential challenges and evaluate risk more effectively, allowing you to make data-driven choices and invest with greater confidence.
Ready to streamline your real estate syndication process and manage your investments with ease? Homebase offers a comprehensive platform designed to simplify fundraising, investor relations, and deal management. Visit Homebase today to learn more.
Share On Linkedin
Share On Twitter
Share On Linkedin
Share On Twitter
DOMINGO VALADEZ is the co-founder at Homebase and a former product strategy manager at Google.
What To Read Next
A Syndicator's Guide to Commercial Real Estate Valuation
Blog
Master commercial real estate valuation with our syndicator's guide. Learn the income, sales, and cost approaches to build investor confidence.
Sign up for the newsletter
If you want relevant updates from our team at Homebase, sign up! Your email is never shared.
Sign up for the newsletter
If you want relevant updates from our team at Homebase, sign up! Your email is never shared.
© 2026 Homebase. All rights reserved.