How to Read a K1: Decoding Your Real Estate Tax Documents
How to Read a K1: Decoding Your Real Estate Tax Documents
Learn how to read a K1 form like a pro investor. Discover what those confusing numbers mean and how to maximize your real estate tax benefits.
Domingo Valadez
Jun 13, 2025
Blog
Your K1 Isn't Just Tax Paperwork—It's Your Investment Report Card

Let's be honest, most investors treat their K1 like something they'd rather not deal with. It arrives, gets a cursory glance, and is immediately forwarded to their accountant. But having reviewed hundreds of K1s from real estate syndications, I've noticed something: the investors who really understand their K1s are making the best decisions. Think of your K1 as a direct line of sight into your investment's performance—it's your investment report card. Just like a report card, it shows you the good, the bad, and the potentially ugly.
Unlocking the Secrets of Your K1
So, how do you decipher this thing? It's not as scary as it looks. Consider it a puzzle, where each section reveals a piece of the story. If you stumble upon unfamiliar terms, a Glossary of financial terms can be a lifesaver. Your K1 will mainly show you income, losses, and distributions. But here's the interesting part: these often don't line up with what you see in your bank account. You might be receiving regular distributions but still show a loss on your K1. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing; in fact, it can be excellent from a tax perspective.
Why Your K1 and Bank Statement Don't Match
This difference is often thanks to depreciation, a major tax advantage in real estate. Imagine owning a profitable property that generates cash flow. The IRS allows you to deduct a portion of its value annually, assuming it’s depreciating, even if its value is actually increasing. This depreciation lowers your taxable income, sometimes resulting in a paper loss even while you receive positive cash flow. This is just one of the reasons why understanding your K1 is so important.
It’s crucial to grasp these nuances as they can significantly impact your overall financial health. Managing investments is like assembling building blocks, with each piece contributing to the whole. This ties into the larger concept of financial literacy, which, surprisingly, is declining. The importance of early literacy is highlighted by statistics showing a decrease in reading proficiency among elementary school students. In the US, data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) reveals that less than 40% of students were reading at or above grade level in 2019. This serves as a reminder that continuous learning, even in seemingly unrelated areas, is essential for successful investing.
Beyond the Basics: Spotting Red Flags
Your K1 can also alert you to potential issues. Unexpected income fluctuations, unusual deductions, or discrepancies between your K1 and other investment documents can be warning signs. Learning to read your K1 and identify these red flags early can prevent future headaches (and potentially financial losses). It's about more than just locating the numbers; it's about understanding what they tell you about your investment's performance. Now that we’ve covered the importance of understanding your K1, let's delve into specific sections and how to interpret the information they contain.
Making Sense of Income and Losses (And Why Losses Can Be Good)

Let's be honest, the income and loss section of a K-1 is where most people start to get confused. It's even a place where many accountants stumble. The numbers here tell a different story than your regular distribution checks, and understanding that difference is crucial for smart tax planning.
I've seen properties generating $2,000 in cash flow each quarter, but the K-1 shows a $5,000 loss. Sounds strange, doesn't it? Actually, it's a great tax situation. This happens because of how the IRS handles certain real estate expenses, particularly depreciation.
Decoding the Different Types of Income
Your K-1 breaks down income into several categories. Rental income is pretty straightforward – it's the rent collected. You might also see capital gains if the partnership sold a property. This is the profit from that sale and it's taxed differently. There might be other income types depending on the investment. Getting comfortable with these different income streams is a key part of understanding your K-1.
Another thing that can make your K-1 look very different from your bank account is timing. For example, a major repair at the end of the year might be fully deducted on that year's K-1, even if you paid for it over several months the following year. This can result in a K-1 loss even though your actual cash flow during those months was positive.
Understanding Losses: They're Not Always Bad
Now, let’s talk about those losses. Depreciation, as I mentioned, plays a big role in real estate K-1s. The IRS allows you to deduct a portion of the property's value each year for wear and tear, even if the property value is going up. This can create a "paper loss" that reduces your taxable income. This is generally a good thing.
A broader understanding of your overall financial picture, perhaps using a net worth calculator, can help put your K-1 into context. Understanding your K-1 is important for making informed tax decisions, but sound financial strategy involves looking at the bigger picture.
It’s important to remember though, not all losses are the same. Some losses might be from unexpected costs or lower-than-expected income. Being able to tell the difference is essential. A depreciation-driven loss is typically good news. A loss due to poor management? That's a red flag.
To get a real sense of your return on investment, look beyond cash distributions and at how the income and losses on your K-1 affect your taxes. This is where a knowledgeable real estate tax advisor can be incredibly helpful. They can help you analyze your K-1, understand its tax implications, and plan accordingly.
Tracking these figures year over year is also important. Changes in income, losses, or depreciation can reveal underlying trends about your investment's performance and its long-term viability.
Unexpected Gains: Planning for the Tax Implications
Let’s not forget the good side of real estate investing! Sometimes, your investment does better than expected, resulting in nice gains. But this often means higher taxes, so planning is key. Consider setting aside some of your distributions to cover potential taxes, especially if your investment involves selling property, which could create a large capital gain. Anticipating these situations helps avoid surprises come tax time.
Before we wrap up, let's look at a handy table summarizing common income and loss items you’ll find on your K-1.
Common K1 Income and Loss CategoriesA breakdown of the most frequent income and loss items on real estate K1 forms and their tax implications
This table provides a quick overview of how different items on your K-1 can affect your tax liability. Keep in mind that this isn't an exhaustive list, and the specifics can vary depending on the individual investment. Consulting with a tax professional is always a good idea for personalized guidance.
Depreciation Benefits: Your Secret Tax Weapon
Depreciation. It's probably the single biggest tax advantage in real estate, and yet so many investors get confused by it when they look at their K-1s. Don't let the accounting terms scare you off. Depreciation is putting money back in your pocket by lowering your taxable income.
It works like this: the IRS allows you to deduct a certain amount every year because they assume your property is going down in value, even if its market value is actually climbing! Imagine deducting $10,000 from your taxes simply because the IRS thinks your profitable property is losing value. That, my friend, is the magic of depreciation.
Tracking Your Basis: A Critical Step
Now, as you take depreciation, the depreciable basis of your property goes down. This is the part of your property's value that the IRS considers eligible for depreciation. It's super important to keep track of this adjusted basis, especially when you decide to sell. Why? It directly affects how much profit (and therefore taxes) you’ll owe.
Let's say your original basis was $100,000 and you've taken $20,000 in depreciation. Your adjusted basis is now $80,000. When you sell, this lower basis means a bigger profit on paper, and potentially higher taxes down the line.
Different Depreciation Methods: Maximizing Your Benefits
There are a few different kinds of depreciation you might see on your K-1. Standard building depreciation is usually spread out over 27.5 years for residential properties and 39 years for commercial ones. You might also see bonus depreciation, which allows for much faster depreciation of certain property improvements.
Knowing which method your investment uses is key to understanding your K-1 and your overall tax situation. For a bigger picture look at potential deductions, you might find this helpful: Real Estate Syndication Tax Benefits
Depreciation Recapture: Understanding the Long-Term Implications
Depreciation offers sweet tax breaks up front, but don't forget about depreciation recapture. When you sell, the IRS basically "recaptures" the depreciation you've taken, taxing it as ordinary income. So, while you saved on taxes during ownership, part of your profit from the sale gets taxed.
This is why it's so important to keep accurate records of your depreciation and to factor in recapture when you're looking at potential investment returns. Good record-keeping will save you from costly mistakes and tax headaches later on.
Real-World Scenarios: Putting it all Together
Let's make this real. You invest in a syndication. Your K-1 shows a $5,000 depreciation deduction for the year. This directly reduces your taxable income, which is great! But, it also lowers your adjusted basis. When you sell, that $5,000 will be recaptured.
Understanding this helps you project your actual net profit after taxes and make smarter investment choices. It's all about seeing how the short-term tax benefits play out with the long-term tax consequences.
Speaking of learning and understanding complex topics, I recently read about a fascinating shift in how kids learn to read. Apparently, there's a growing trend called the Science of Reading (SoR) that's being used in schools. This report I came across, the K-12 Reading Market Report 2024, suggests this trend is going to reshape reading instruction and purchasing decisions for educational materials. Kind of a random connection, I know, but it reminded me of how important it is to keep learning and stay informed about changes in different areas—things that might even indirectly impact your investment strategy. Learn more about this educational shift.
Depreciation isn’t just some abstract idea; it's a powerful tool. By grasping how it works on your K-1, you can really maximize those tax benefits and make better investment decisions. Now, let's move on to another key part of your K-1: understanding distributions and your investment basis.
Understanding Distributions and Your Investment Basis
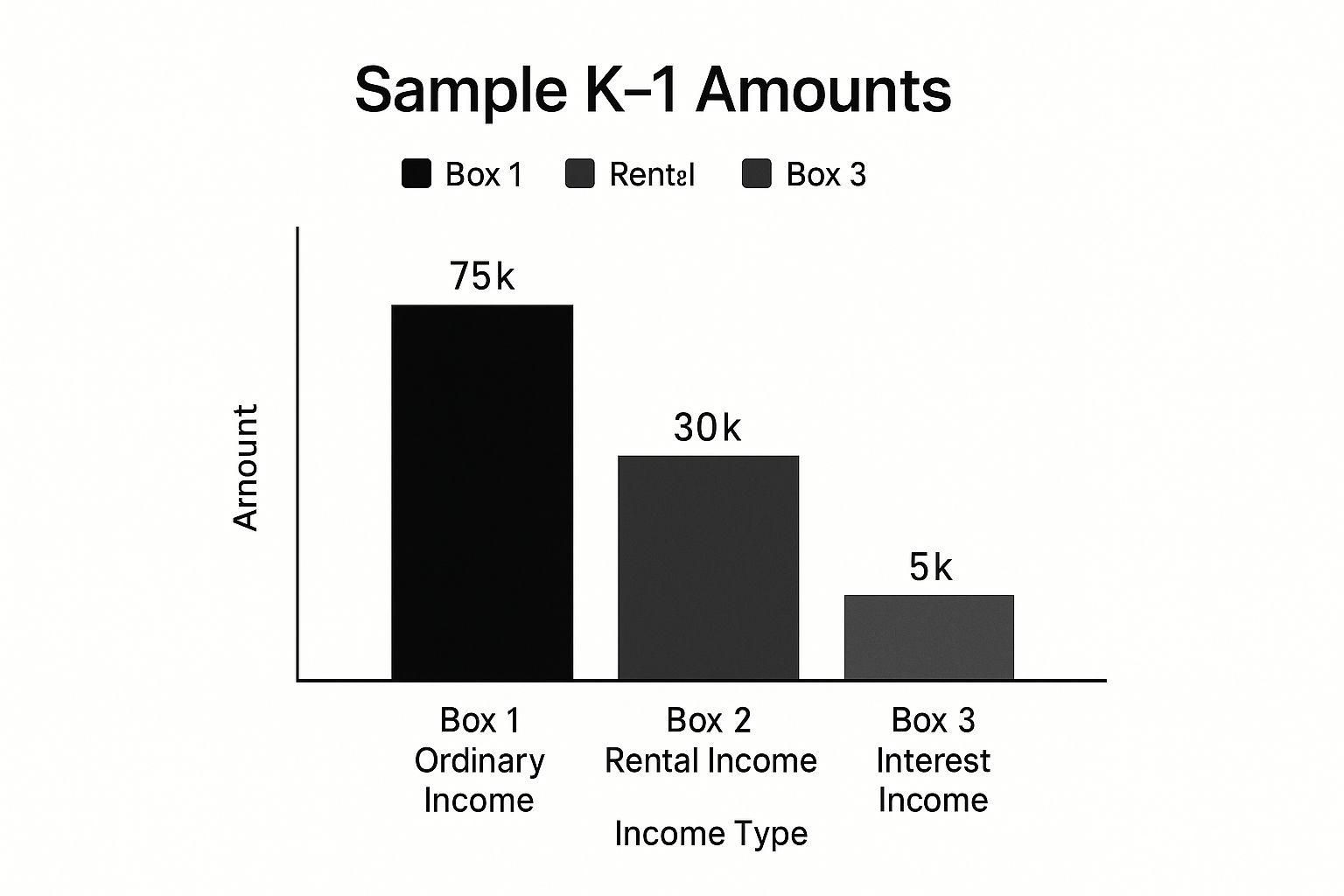
This infographic breaks down a sample K-1, showing $75,000 in ordinary income, $30,000 in rental income, and $5,000 in interest income. Notice how much of that is ordinary income? That's why knowing how each income stream is treated on your K-1 is so important.
One of the trickiest things about K-1s is that getting a distribution doesn't automatically mean it's taxable income. I've seen investors mistakenly celebrate a big distribution, only to be surprised by a hefty tax bill later on. Knowing your investment basis is key to avoiding this. Think of your basis as the amount of your own money you've put into the deal that's "at risk."
Three Types of Distributions: Not All Created Equal
Distributions generally fall into three buckets: return of capital, operating income distributions, and capital gain distributions. Return of capital is simply getting your initial investment back. It lowers your basis but isn't taxed. It's not profit, so the IRS doesn't consider it income.
Operating income distributions, on the other hand, are taxable. This is the profit from the property’s day-to-day operations—think rent. If the property generates $10,000 in profit and you're entitled to half, your $5,000 share is taxable, usually as ordinary income. Lastly, capital gain distributions are profits from the sale of a capital asset, like the property itself. The good news? These are typically taxed at the lower capital gains rates.
Tracking Your Basis: Avoiding Tax Surprises
So, how do you know what kind of distribution you’ve received? By tracking your basis! Every time you receive a return of capital distribution, your basis goes down. Let's say you invest $100,000 and get a $10,000 return of capital distribution. Your new basis is $90,000. Anything you receive above your original investment is usually taxable, even if it's labeled "return of capital." This is where precise record-keeping becomes absolutely essential.
Real-World Examples: How Distributions and Taxes Interplay
Imagine receiving a $50,000 distribution. Sounds amazing, right? But what if $40,000 of that was return of capital? You'd only owe taxes on $10,000. Conversely, you could receive a smaller $10,000 distribution, but if your basis is already zero, the entire amount is taxable. See why you need to understand both distributions and basis to really grasp your K-1?
Negative Capital Accounts and Their Tax Implications
Things can get complicated if you have a negative capital account. This can happen when losses (sometimes from depreciation) are greater than your initial investment. A negative capital account impacts how future distributions are taxed and can even have implications when you sell your interest. If this happens to you, definitely talk to a tax professional. Distributions exceeding your basis can be difficult to interpret, especially with negative capital accounts involved.
Key Takeaways for Smart Tax Planning
Understanding the link between distributions and your basis is crucial for reading and interpreting your K-1. It helps you anticipate your tax liability, avoid unpleasant surprises, and make smart investment choices. By keeping good records and understanding the different distribution types, you’ll be much better equipped to manage your taxes and maximize your returns. Don't just pass your K-1 to your accountant—take the time to understand it. This knowledge is powerful and will help you take control of your financial future.
This table, "Distribution Types and Tax Treatment", summarizes how different distributions from real estate investments are handled for tax purposes and how they impact your basis. Keeping these distinctions clear will make tax season much less stressful. Remember, accurate record-keeping is your best friend when it comes to navigating the complexities of K-1s.
Navigating the Multi-State Tax Nightmare

If you're dabbling in real estate syndications, your properties are likely scattered across different states. This is where deciphering your K-1 gets extra interesting—multi-state taxes. Trust me, it can be a real pain, especially if you live in a high-tax state and invest elsewhere.
Understanding Multi-State Filing Requirements
So, when do you actually need to file in multiple states? Simply put: if you make money in a state, they'll probably want their share, regardless of where you live. If your syndication has property in Texas, California, and New York, you're likely looking at filing in all three, even if you're based in Florida. It can get confusing quickly, so understanding the basics is key.
Avoiding Double Taxation
The biggest fear with multi-state filing? Double taxation. Luckily, most states have ways to prevent this, usually through a credit for taxes paid elsewhere. This isn't always simple though, as each state calculates these credits differently. Solid record-keeping is essential here—proper documentation is your best friend in case of any discrepancies or audits.
Real-World Examples: Navigating State-Specific Rules
Let me give you a few examples. Imagine living in California (high-tax) and investing in a property in Texas (no state income tax). You'll file in California, but you won't owe Texas anything. Now, switch the investment to New York. You'll owe both states. California will give you a credit for the New York taxes, but it may not cover the full amount. See how this can get tricky? It highlights the fact that states have very different tax laws. These differences extend beyond just taxes too. Ever think about how reading levels vary internationally? It's fascinating! The Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS) actually dives into this global variation.
Reciprocity Agreements: A Potential Simplification
Some states have reciprocity agreements, where residents of one state working in another don't pay taxes to the work state. This might apply to K-1 income sometimes, but it's not common and depends entirely on the specific state rules. Don't assume reciprocity automatically wipes out your multi-state filing requirements. You have to check the fine print for each state and your investment type.
Estimating Your Total Tax Burden
Figuring out your total tax bill across multiple states takes some effort. You'll need to account for each state's individual rules, possible credits, and any reciprocity agreements. A spreadsheet can help you track everything, or you might consider software specifically designed for multi-state tax calculations.
When to Hire a Tax Professional
Multi-state tax filing can become a tangled web fast. If you're juggling investments in several states, or the rules around credits and reciprocity seem unclear, a tax pro is worth their weight in gold. A specialist in multi-state real estate investing can save you headaches and potentially a lot of money. They'll help you navigate the complexities of each state, make sure you're taking all the credits you can, and help you avoid expensive mistakes. Remember, with complicated tax situations, expert advice is an investment, not a cost. Now that we've tackled this beast, let’s move on to spotting those red flags on your K-1.
Red Flags and When Your K-1 Is Telling You Something's Wrong
After looking at more K-1s than I care to remember, I've gotten pretty good at spotting potential issues. Let's be honest, not every K-1 is a work of art. Sometimes, the numbers are practically shouting that something isn't right with your investment. So, let's walk through some real-life examples of what can go wrong and, more importantly, how to interpret what you're seeing.
Common Errors and What They Mean
One thing I see all the time is plain old calculation errors. Maybe the total distributions don't add up to the individual amounts listed, or perhaps the depreciation calculation seems a bit off. These kinds of errors are usually just annoying oversights, but they warrant a follow-up question to the syndicator.
This screenshot shows the different K-1 forms out there. It’s a good reminder to make absolutely sure you have the right one—the one for partnerships (Form 1065). Real estate syndications are partnerships, so that's the form you should be receiving. Getting the wrong one can mess up your taxes big time.
Now, the really concerning red flags are the ones that show a mismatch between your K-1 and your original investment documents. For example, let's say your operating agreement clearly states you get a 50% split of the profits. But then your K-1 shows up, and you're only getting 40%. Houston, we have a problem. That's a serious discrepancy that needs immediate clarification. It could indicate a real issue with how the syndicator is handling the money.
Another thing to keep a close eye on is depreciation. If the depreciation claimed seems way higher or lower than you’d expect based on the property's type and age, dig a little deeper. Overstated depreciation can come back to bite you with a hefty tax bill down the road, while understated depreciation means you might be missing out on valuable tax breaks.
Timing Issues and Discrepancies
Late K-1s are a headache, especially when tax season is breathing down your neck. Consistently late filings, or constantly needing amendments to previous K-1s, could signal organizational problems within the syndication. Lots of amendments might mean they're not paying attention to details, or worse, there could be deeper accounting issues. If you see this happening repeatedly, it's worth considering the sponsor's overall competence.
Another red flag? Inconsistencies between your K-1 and what the syndicator has been telling you. If you were expecting a big capital gain based on the sponsor's updates, but your K-1 shows little to no gain, or even a loss, pick up the phone. Transparency is crucial in real estate syndications. Unexplained discrepancies erode trust faster than anything.
Verifying Your K-1: Asking the Right Questions
Never hesitate to contact the syndicator if you have questions. A good sponsor will be happy to clear up any confusion and provide documentation. It’s smart to have a list of specific questions ready about anything that concerns you. Don't be shy about asking for detailed explanations and supporting documents, especially for anything that seems unusual.
Here are a few questions to get you started:
- Can you explain the difference between the projected returns and the numbers on my K-1?
- I noticed the depreciation is lower than I anticipated. How was it calculated?
- My K-1 was late this year. What are you doing to make sure it’s on time next year?
If the syndicator avoids your questions or can't give you straight answers, it might be time to bring in the professionals.
When to Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, figuring out a K-1 is more complicated than just asking a few questions. Complex issues or discrepancies that just won’t go away might require a tax attorney or a CPA specializing in real estate partnerships. Yes, it's an extra expense, but the peace of mind and potential tax savings can be well worth it. Think of it as an investment in protecting your investment.
Your Practical K1 Action Plan for Tax Season and Beyond
So, you've got a handle on what your K1 is telling you. Great! Now let's talk about actually using that information. This isn’t just about getting through tax season – it’s about using your K1 as a tool for smarter investing all year round.
Organizing Your K1 Information: A System for Success
Picture a filing cabinet just for your K1s. Not exactly exciting, right? But a good organizational system is pure gold. It can save you hours of frustration and potentially a lot of money. A simple spreadsheet works wonders for tracking the key figures from each K1: income, losses, distributions, and your adjusted basis. This makes comparing performance across investments super easy and helps you see trends over time.
Personally, I use a cloud-based system. Being able to access my K1 info from anywhere has been a lifesaver, especially when I’m meeting with my tax advisor or checking out potential new investments. Having everything organized and accessible is priceless.
Working with Your Tax Preparer: Asking the Right Questions
Your tax preparer isn't a mind reader. They need context. Don’t just hand them your K1; explain the investment it represents. A checklist of questions can be really helpful in guiding the conversation and making sure they consider all the tax implications. For example, ask them about specific depreciation strategies and how they're maximizing your deductions.
Here’s a pro tip: ask your tax preparer about their experience with real estate syndications specifically. Not all CPAs are the same, and you want someone who understands the nuances of these investments.
Estimating and Planning for Tax Liability
K1 income can be a bit unpredictable, so tax planning is crucial. Use your organized K1 data to estimate your tax liability throughout the year. This way, you can make quarterly estimated tax payments and avoid penalties and surprises at tax time. Trust me, I learned this one the hard way. Underestimating K1 income can lead to a hefty tax bill.
Record Keeping: Making Future Years Easier
When it comes to K-1s, good record-keeping is your best friend. Keep copies of everything: your original investment documents, all your K1s, and any communication with the syndicator. A well-organized record system simplifies future tax filings and gives you the documentation you need if you're ever audited. It's not just about compliance; it's about protecting your investments.
Using Your K1 to Evaluate Sponsor Performance
Your K1 is more than just a tax document; it’s a performance report for your sponsor. Compare the actual results on your K1 to the sponsor's projections. Consistent underperformance? Big red flag. On the other hand, a sponsor who consistently beats projections demonstrates strong management and could offer lucrative future opportunities.
Comparing Different Investments and Identifying Trends
Use your K1 data to compare how your various real estate syndication investments are performing. Are some consistently doing better than others? Are certain types of properties generating higher returns? Seeing these trends helps you shape your future investment strategy and put your money into the most promising opportunities. This data-driven approach removes the emotion from investing and helps you make smart decisions.
By using these practical strategies, you can transform your K1 from a confusing tax document into a powerful tool for building wealth through real estate. Want to simplify your real estate syndication process and K1 management? Check out Homebase – the all-in-one platform built for real estate sponsors. From fundraising to investor relations, Homebase simplifies everything.
Share On Linkedin
Share On Twitter
Share On Linkedin
Share On Twitter
DOMINGO VALADEZ is the co-founder at Homebase and a former product strategy manager at Google.
What To Read Next
A Guide to Real Estate Financial Modelling for Syndicators
Blog
Master real estate financial modelling with this guide. Learn to build models that analyze deals, forecast returns, and build unwavering investor confidence.
Sign up for the newsletter
If you want relevant updates from our team at Homebase, sign up! Your email is never shared.
Sign up for the newsletter
If you want relevant updates from our team at Homebase, sign up! Your email is never shared.
© 2026 Homebase. All rights reserved.